VACUUM GLASS HELPS UPVC WINDOWS TO ACHIEVE CARBON NEUTRALITY
1 building energy efficiency standard requirements
Beijing's "Design Standard for Energy Efficiency of Residential Buildings" was officially implemented on January 1st, 2021, which raised the energy efficiency rate of residential buildings in Beijing from 75% to over 80%, marking the building energy efficiency to a higher level.
China's building energy conservation is based on the building energy consumption from 1980 to 1981, and the energy efficiency is increased by 30% in each step on the basis of the previous stage as a stage:
The first step of energy saving is to save 30% on the basis of 1980-1981, which is commonly referred to as the standard of 30% energy saving.
The second step of energy saving is to save 30% on the basis of the first step of energy saving, that is, 1-(0.7*0.7)=51%. (For the sake of making it easier to express literally, the state has set the energy saving rate as 50%).
The third step of energy saving is to save 30% on the basis of the second step, that is, 1-(0.7*0.7*0.7)=66%, which is referred to as the standard of energy saving of 65% for short.
The fourth step of energy saving is to save 30% on the basis of the third step of energy saving, that is, 1-(0.7 * 0.7 * 0.7) = 76%, which is referred to as the standard of 75% energy saving for short.
According to this calculation, the fifth step of energy saving is to save 30% on the basis of the fourth step of energy saving, that is, 1-(0.7 * 0.7 * 0.7 * 0.7) = 83%.
The overall energy saving target has been significantly improved: from the original 75% to over 80%. The thermal performance of building envelope is improved, and the standard of heat transfer coefficient of external windows is greatly improved: the heat transfer coefficient k value of external windows, balcony doors (windows), light-transmitting parts of curtain walls and roof skylights is set to be no more than 1.1w/(m2 k).
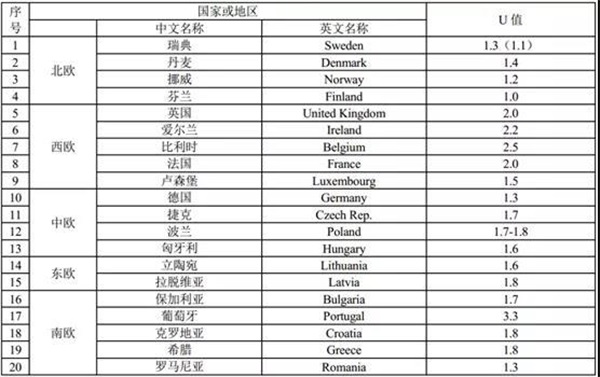
According to relevant statistics, the requirement that the heat transfer coefficient k value of doors and windows in Beijing is lower than 1.1w/(m2 k) has reached the requirement of building with near zero energy consumption, and has reached the leading level in European countries. (see table 1)
Table 1 Limits of U values of external windows in European countries or regions
The term "Nearly zero energy building" originated from the European Union. On July 9, 2010, the European Union issued the Energy Performance of Building Directional Recast (EPBD), which requires all member states to ensure that all new buildings owned or used by the government meet the requirements of "near zero energy consumption buildings" from December 31, 2018; From December 31, 2020, all new buildings will meet the requirements of "near zero energy consumption building". Due to the unbalanced economy and large span of climate zones in EU member states, member states can put forward their quantitative goal of "near-zero energy consumption" building on the basis of their own actual situation and on the premise of fully considering the cost-benefit ratio of energy-saving technologies, but there is no unified and clear quantitative energy-saving goal. For "near-zero-energy-consumption building", there are different specific definitions in EU countries.
At present, many domestic door and window enterprises have applied for the window component certification certificate of passive house Institute (PHI). The requirement of PHI for windows is that Uw value should be less than 0.8 W/(㎡ k). (This refers specifically to the climate zone where Beijing is located)
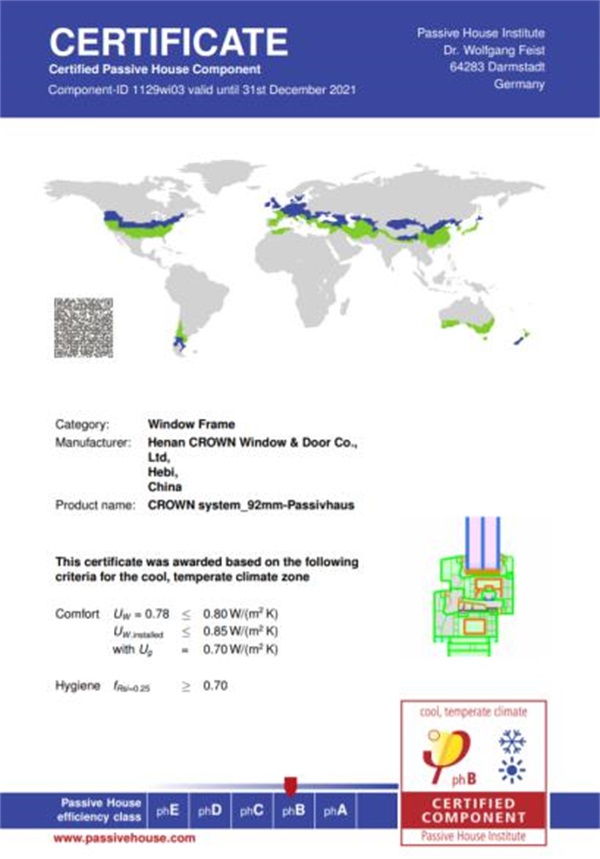
Figure 1 PHI certification certificate
2 Thermal simulation calculation and analysis
2.1 Differences between calculation results of European standards and Chinese standards
First of all, we need to analyze the difference between the calculation results of European standard and Chinese standard: "6 double silver LowE+16Ar+5+16Ar+6 double silver lowE" is selected for glass preparation. The value of the heat transfer coefficient k in the central area of the glass calculated by JGJ151 is 0.709W/(㎡ k); If the heat transfer coefficient k value of the central area of the glass calculated by CEN standard is 0.603W/(㎡ k). Using two standards and Crown92 series UPVC profiles respectively, the calculation results of the whole window heat transfer coefficient Uw are as follows:
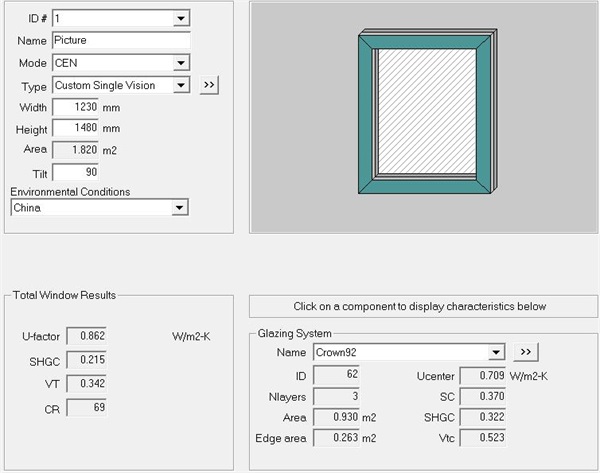
Figure 2 The whole window Uw calculated using Chinese standard is 0.862.
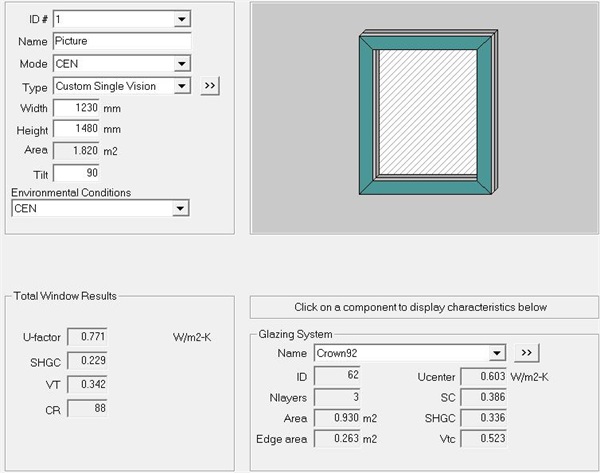
Figure 3 The whole window Uw calculated using European standard is 0.771.
Compared with the calculation results, it can be found that the calculation results of the whole window heat transfer coefficient Uw will be different because of the different calculation standards for the same windows.
2.2 Comparison of U values of windows made of different materials
Therefore, all the configurations discussed in the following article are simulated under the environmental conditions of the Chinese standard (JGJ/T151-2008 Code for Thermal Calculation of Glass Curtain Wall of Building Doors and Windows):
First of all, for the 70 series of broken bridge aluminum, U-PVC and wooden windows that are common in the market, on the premise of the same window type and the same glass configuration (see Figure 4 for details), the comparison results are shown in Figure 5~ Figure 7:
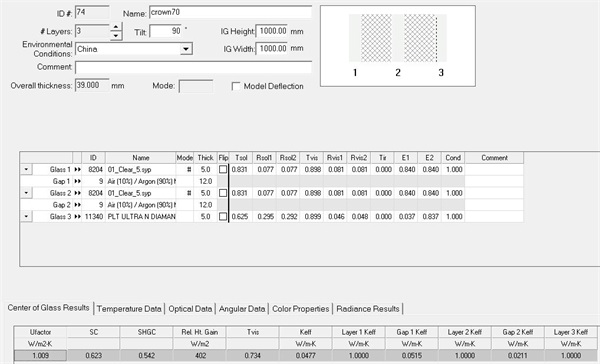
Fig. 4 Glass configuration of insulating glass
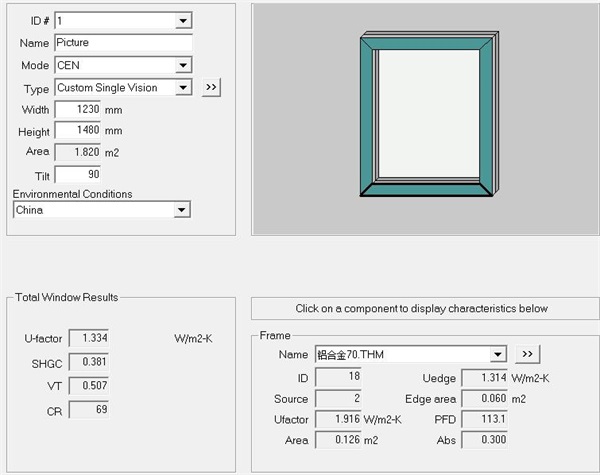
Fig. 5 The calculation result of 70 series aluminum alloy window with broken bridge is: 1.334 W/(㎡ k)
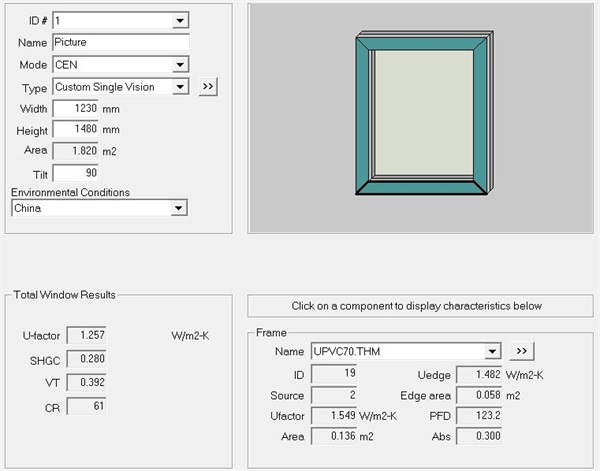
Fig. 6 The calculation result of 70 series U-PVC window is: 1.257W/(m2 k)
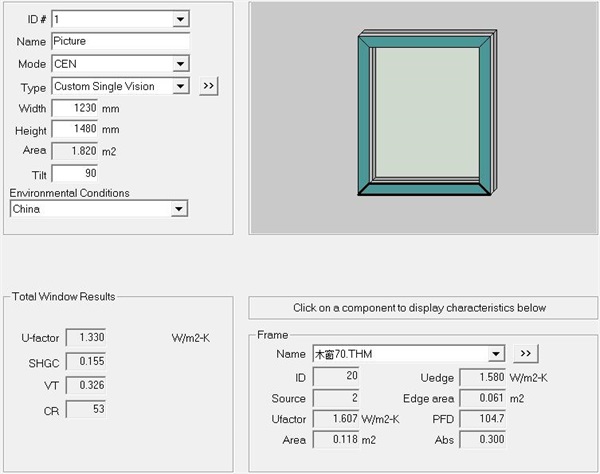
Fig. 7 The calculation result of 70 series wooden windows is: 1.330w/(m2 k)
In summary, it can be seen from the simulation results that the Uf value of profiles of U-PVC windows of the same series of doors and windows is the lowest, and the heat transfer coefficient of the whole window is also the lowest when the glass configuration is the same.
2.3 Replace the insulating glass configuration and window type to reduce the U value of the whole window.
There is still a certain distance between 1.257W/(㎡ k) and the whole window heat transfer coefficient of 1.1W/(㎡ k). Next, first try to upgrade the configuration of insulating glass, and reduce the K value of insulating glass from about 1.0 W/(㎡ k) to about 0.8 W/(㎡ k). (See Figure 8) Recalculate whether 70 series UPVC windows can meet the energy-saving design requirements of residential buildings in Beijing.
Through the simulation calculation of a simple window with a size of 1230mm*1480mm, the simulation result of the whole window heat transfer coefficient Uw is 1.110w/(㎡ k) (see Figure 9). Then, replace the specifications with the left and right partition windows of 1500mm*1500mm, and continue to use JGJ/T 151 for calculation:
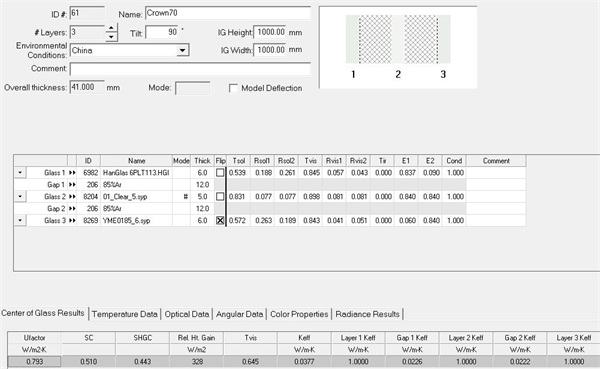
Fig. 8 Glass configuration of insulating glass
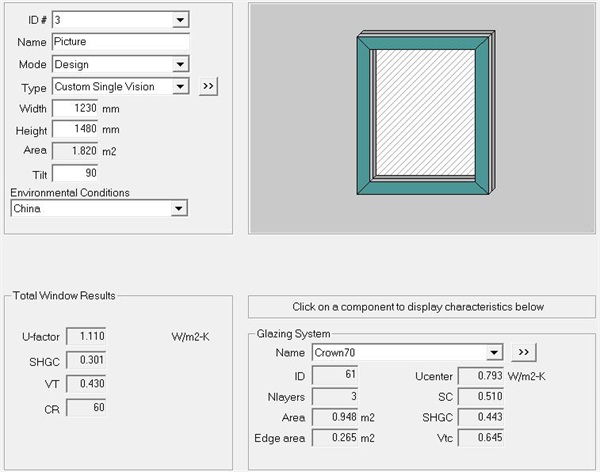
Fig. 9 Calculation result of 1230mm * 1480mm window type
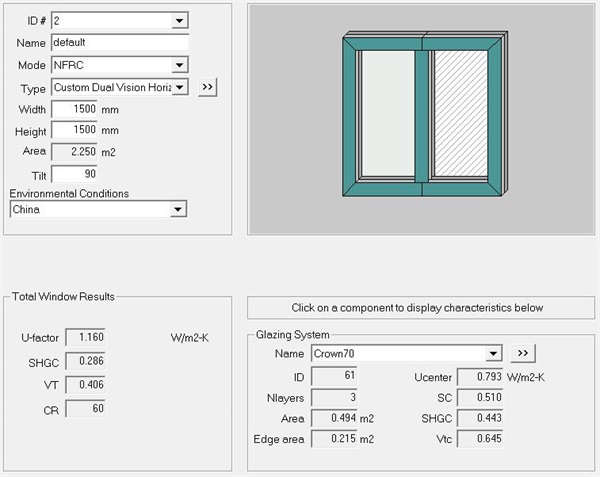
Figure 10 Calculation result of 1500mm * 1500mm window type
Through calculation, the simulation result of the whole window heat transfer coefficient Uw is 1.160W/(m2 k) (see Figure 10 for details). Therefore, 70 series UPVC windows with traditional insulating glass obviously can't meet the requirements of Beijing residential building energy-saving design code.
2.4 Adopt vacuum glass to further reduce the U value of the whole window.
Vacuum glass is a new type of glass deep processing product, which is developed based on the principle of thermos bottle. The structure of vacuum glass is similar to that of hollow glass, but the difference is that the gas in the cavity of vacuum glass is very thin, almost close to vacuum. Vacuum glass is to seal the periphery of two pieces of flat glass, vacuumize the gap and seal the vent hole. The gap between the two pieces of glass is 0.3mm Generally, at least one of the two pieces of vacuum glass is low-emissivity glass, so that the heat lost through the conduction, convection and radiation of vacuum glass can be minimized. Its working principle is the same as that of glass thermos. Vacuum glass is the fruit of cooperation between glass technology and material science, vacuum technology, physical measurement technology, industrial automation and building science, etc., and a variety of disciplines, technologies and processes.
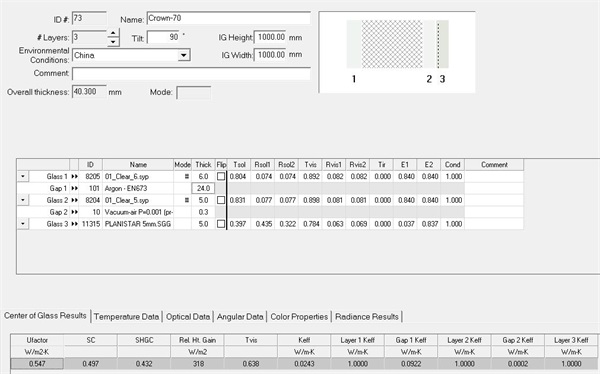
Fig. 11 Configuration of vacuum composite insulating glass
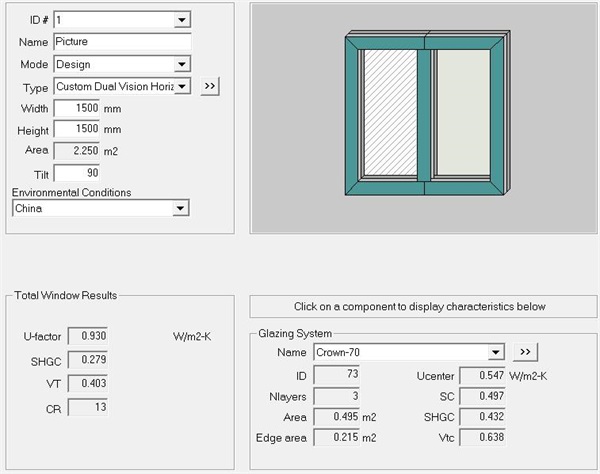
Figure 12 Calculation results of 1500mm * 1500mm window type
With 70 series UPVC windows with vacuum composite insulating glass, the same 1500mm*1500mm left and right partition windows are also calculated according to JGJ/T 151, and the calculation result of the whole window heat transfer coefficient Uw is 0.930w/(m2 k). (See Figure 12 for details)
Finally, in order to more accurately simulate the whole window heat transfer coefficient of "T" separated 1500mm*1500mm standard window, due to software limitations, the window can only be divided into upper and lower parts. (Due to the limitation of Window software, the heat transfer coefficient of "T"-shaped separated window cannot be calculated.) The height of the upper half is 500mm, and the height of the lower half is 1000mm. After calculating the whole window heat transfer coefficients of the upper and lower parts in turn, the final whole window heat transfer coefficient is obtained by the area weighted summation formula.
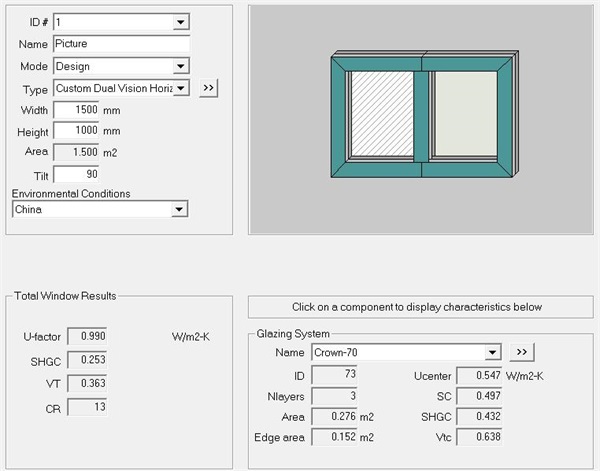
Fig. 13 Calculation results of the lower part
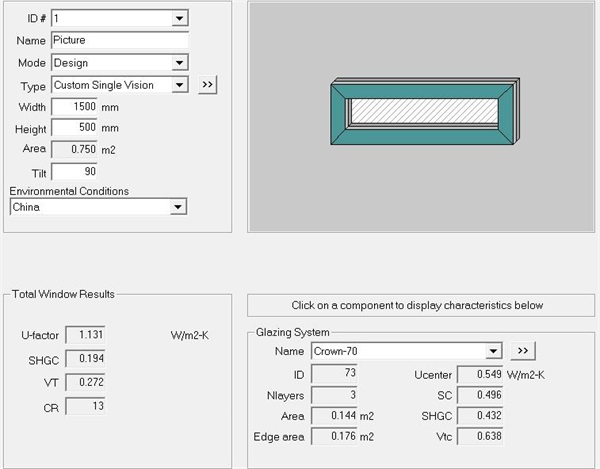
Figure 14 Calculation results of the upper part
After area weighting calculation, UW = (0.99 * 1.5m2+1.131 * 1.5m2)/2.25m2 = 1.03W/(m2 k). (See Figure 15 and Figure 16 for the simulated temperature curve and heat flow curve.)
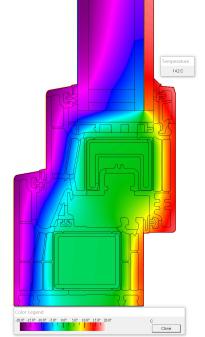
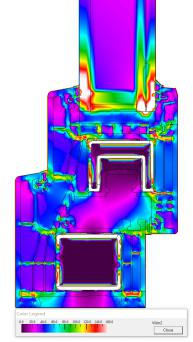
Fig. 15 Crown70 series temperature curve fig. 16 Crown70 heat flow curve
To sum up, Uw of 70 series UPVC windows equipped with vacuum glass has reached 1.03W/(m2 k), which can easily meet the requirements of Beijing residential building energy efficiency design code. When the vacuum glass configuration is upgraded to double Low-E vacuum composite insulating glass, the Uw value can be less than 1.0 W/(m2 k). It can meet the energy-saving requirements of passive ultra-low energy consumption residential buildings in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, Shandong province, Henan province and the three eastern provinces. At the same time, it also meets the energy-saving requirements of near-zero energy consumption buildings in severe cold areas and cold areas. (See Figure 17 for details)
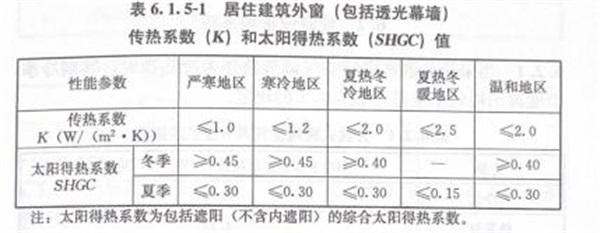
Fig. 17 Technical Standards for Near Zero Energy Consumption Buildings
Finally, the author replaced the glass configuration of PHI-certified "passive window" with double Low-E composite vacuum insulating glass, and made thermal calculation. The simulation result of the whole window heat transfer coefficient Uw was 0.652 W/(m2 k) (see Figure 18 for details).
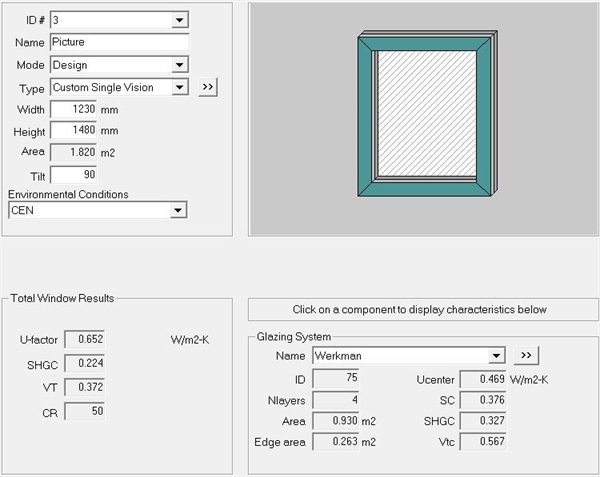
Fig. 18 Calculation results of 1230mm * 1480mm PHI window type
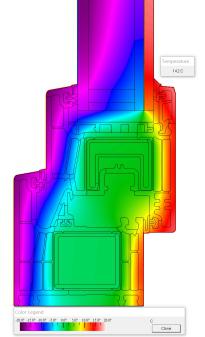
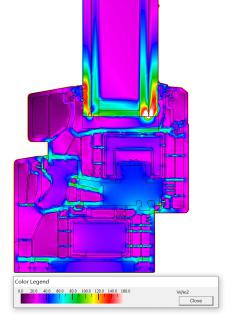
Fig. 19 Crow92 series temperature curve fig. 20 Crow92 heat flow curve
3 Conclusion
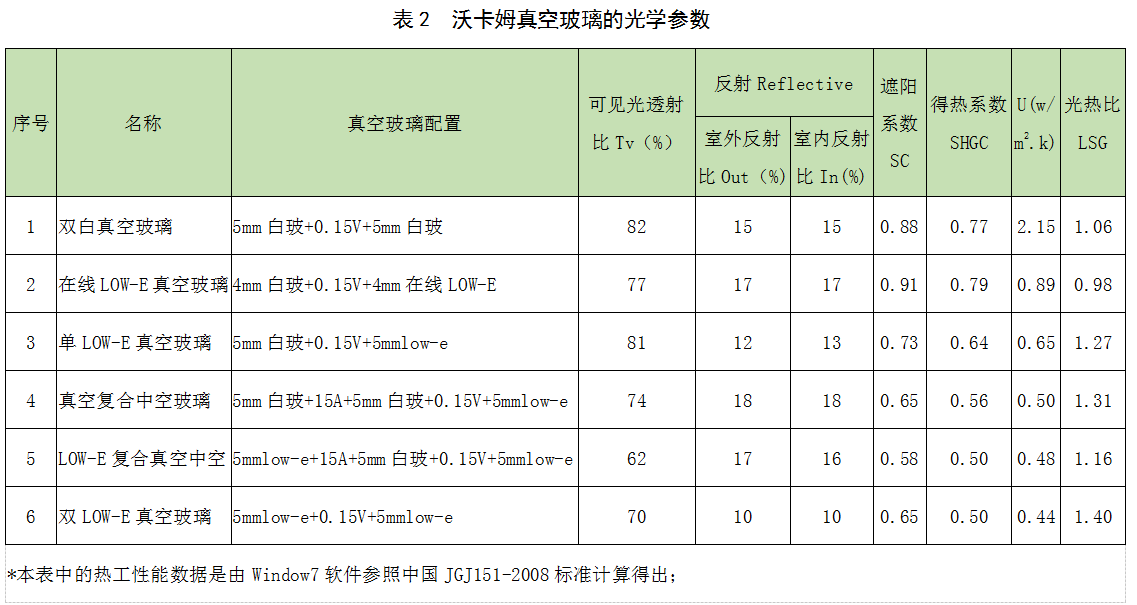
Through the above series of calculations, it can be found that: for insulating glass, the insulation performance of different spacer layers is also different. The thermal insulation performance of real space insulation layer is far superior to that of traditional space insulation layer, and the heat transfer coefficient of vacuum composite insulating glass is much lower than that of traditional insulating glass. (See Table 2 for details)
UPVC profile with excellent performance, combined with vacuum glass equipped with Low-E and warm edge spacer, finally made high-performance doors and windows with excellent thermal insulation performance. Vacuum glass can not only effectively improve the thermal insulation performance of doors and windows, but also reduce the total thickness of hollow composite glass and the thickness of profiles, thus reducing the self-weight of glass and whole windows, and indirectly prolonging the life of hardware and whole windows. At the same time, the unique vacuum degree maintaining technology of Werkman vacuum glass fully guarantees the durability of the glass. When China is faced with two unprecedented challenges of "2030 peak carbon dioxide emissions" and "2060 carbon neutrality", improving the energy-saving performance and durability of UPVC windows can effectively help the vigorous development of near-zero energy consumption buildings and passive buildings.
Author introduction
Liu Yongliang, general manager of Werkman (Shandong) Vacuum Glass Technology Co., Ltd.; Address: Building 1, Zhongrun Fortune Center, Lixia District, Jinan City, Shandong Province; Tel: 13793298222; Email: 99597556@qq.com